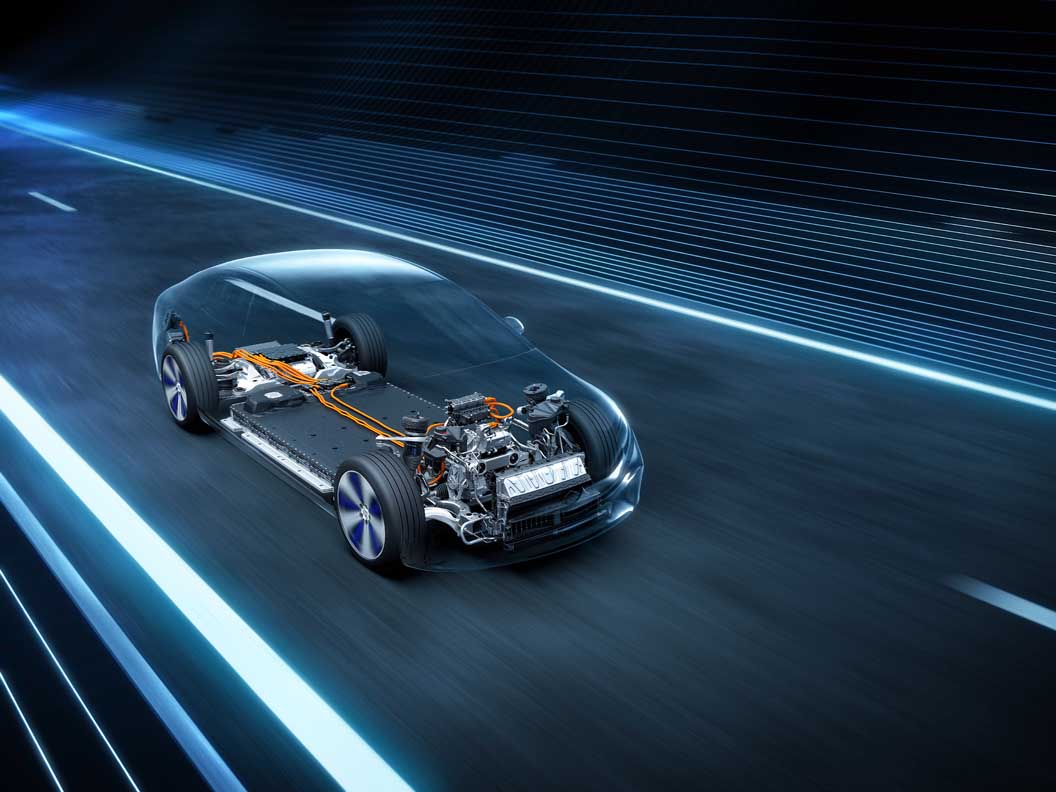
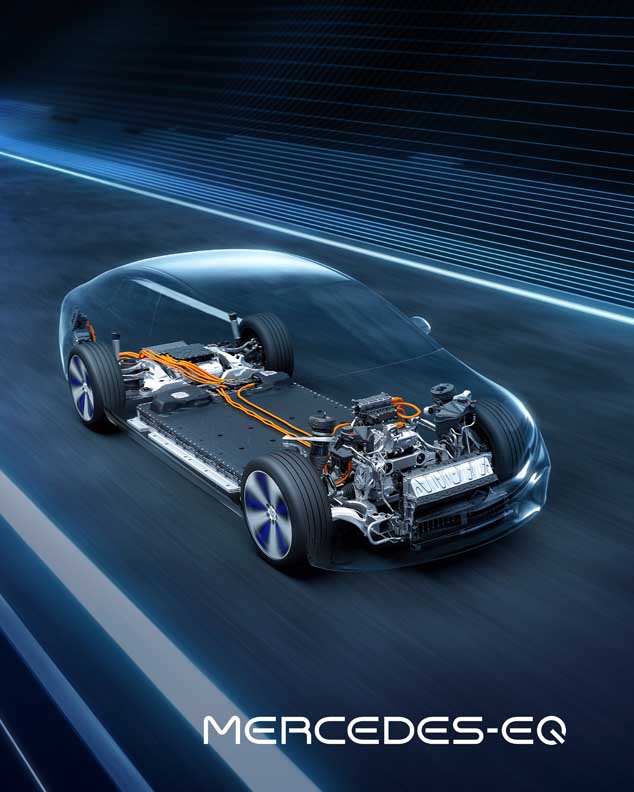
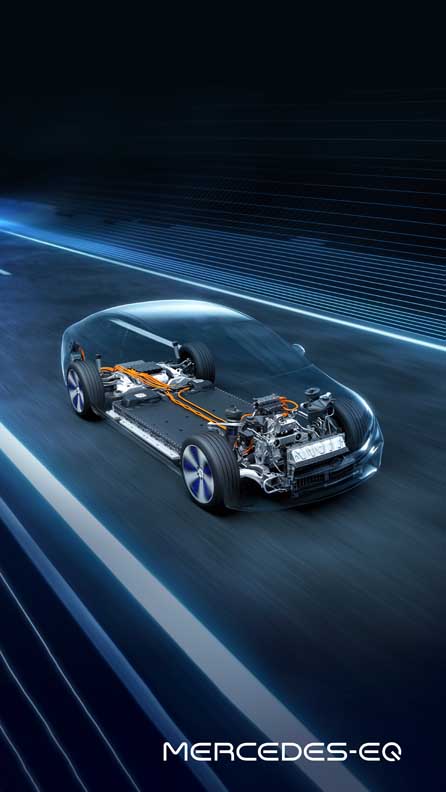
The EQS is the stand-alone, all-electric member of the new S-Class range and will be launched in Europe in August. With the EQE business saloon and the SUV variants of the EQS and EQE, further models based on the new architecture will follow soon.
The EQS will allow customers in the luxury segment to benefit fully from all the advantages of an all-electric architecture with respect to space and design. With ranges of up to 770 km (according to WLTP)1, the EQS meets the requirements on a progressive saloon in the S-Class segment in this respect as well. The new world record in aerodynamics for production cars with a cd value of 0.202 contributes significantly to this.
The new generation of electric vehicles in the luxury and executive segment is based on a custom-developed architecture, which is scalable in every aspect and can be used across model series.
The wheelbase and track as well as all other system components, especially the batteries, are variable thanks to the modular design. The vehicle concept is thus optimised to meet every requirement of a future-oriented, battery-electric model family.

No cable reaches this far
Electric drive system3: non-stop from Munich to Berlin
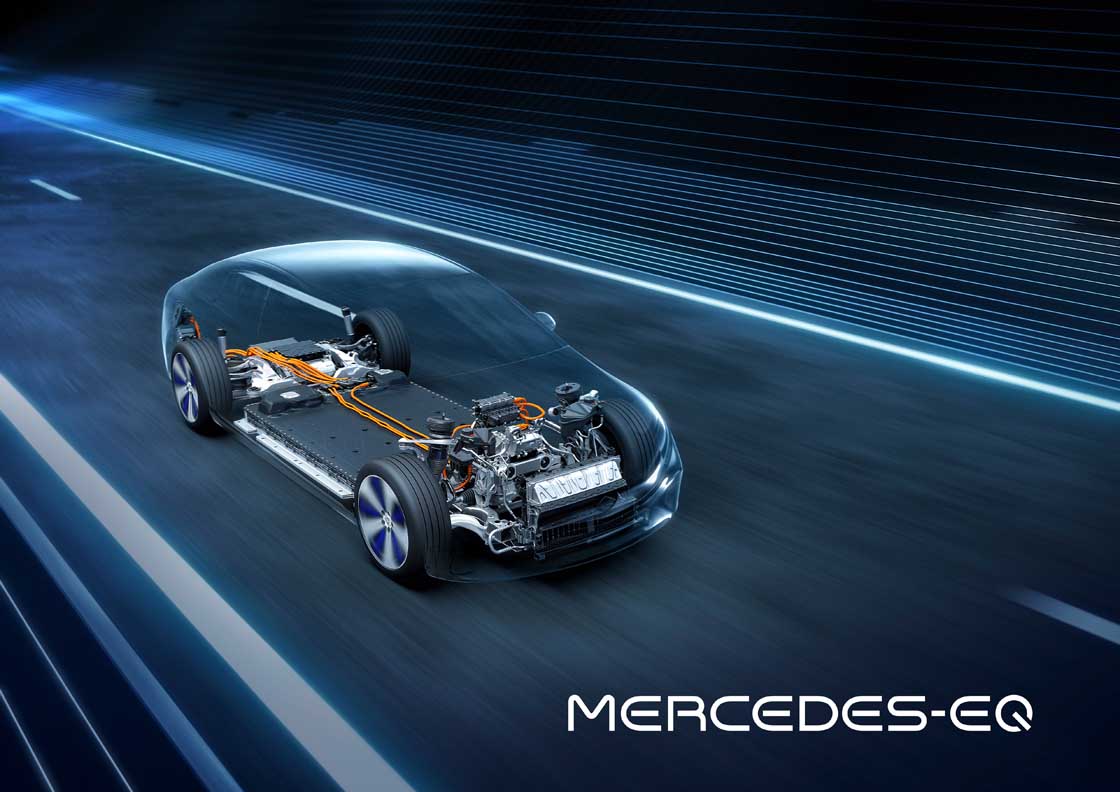
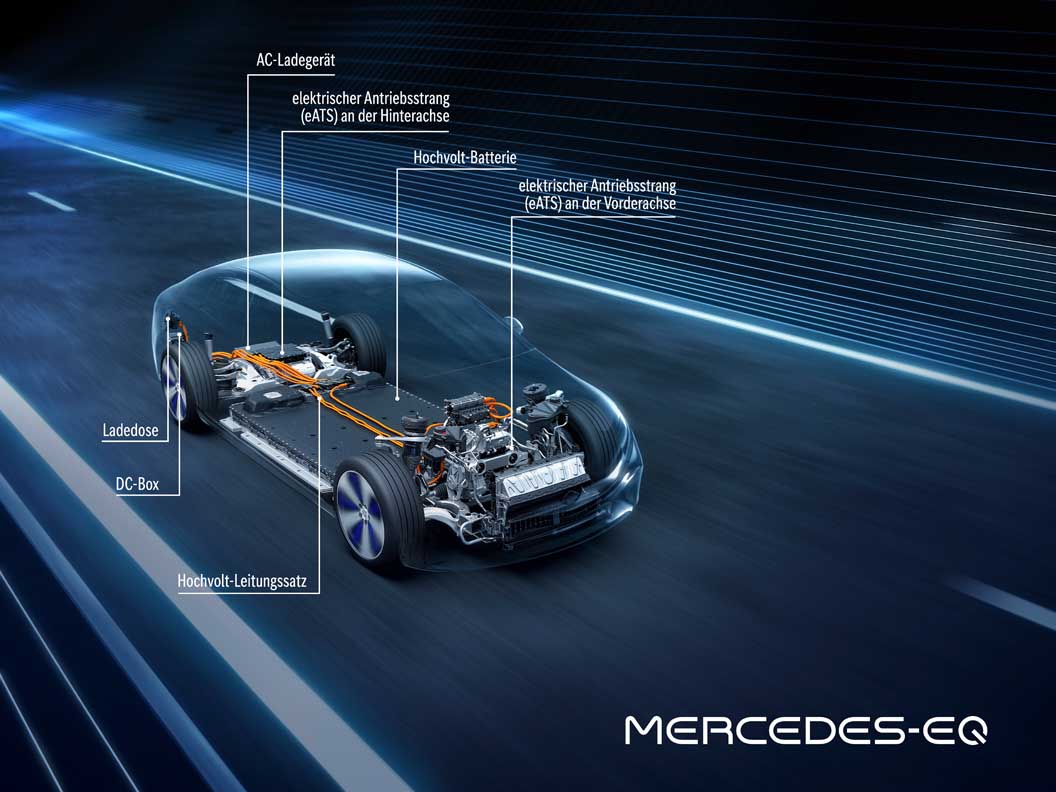
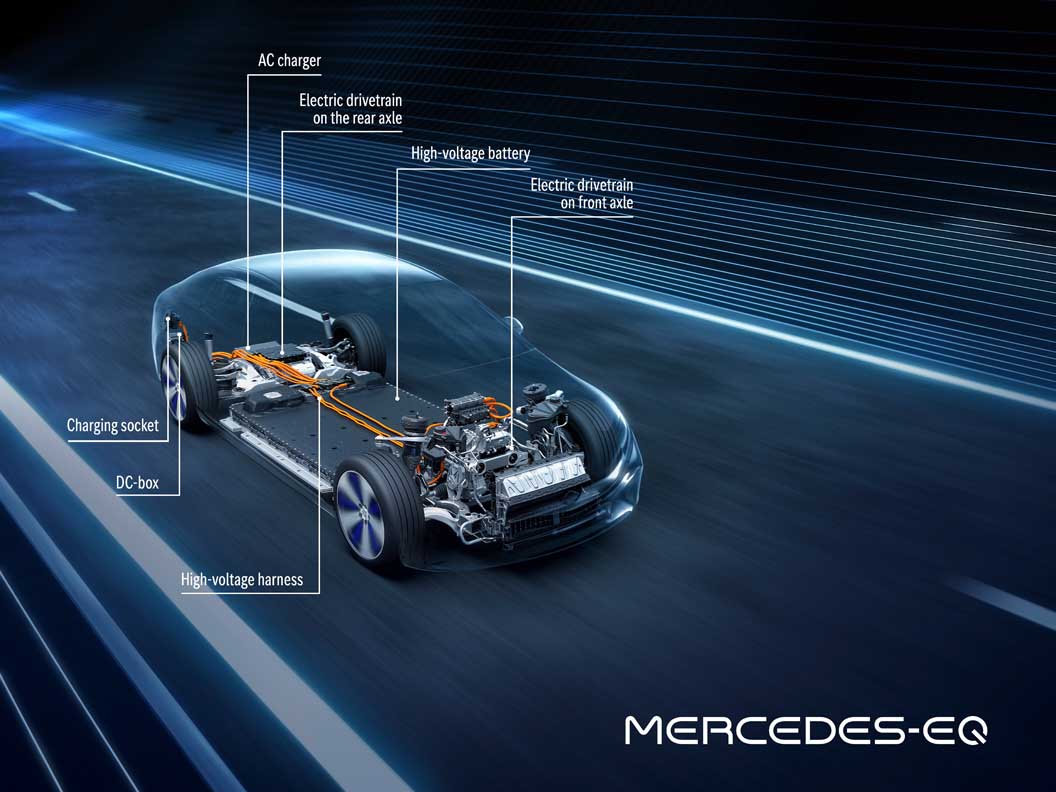
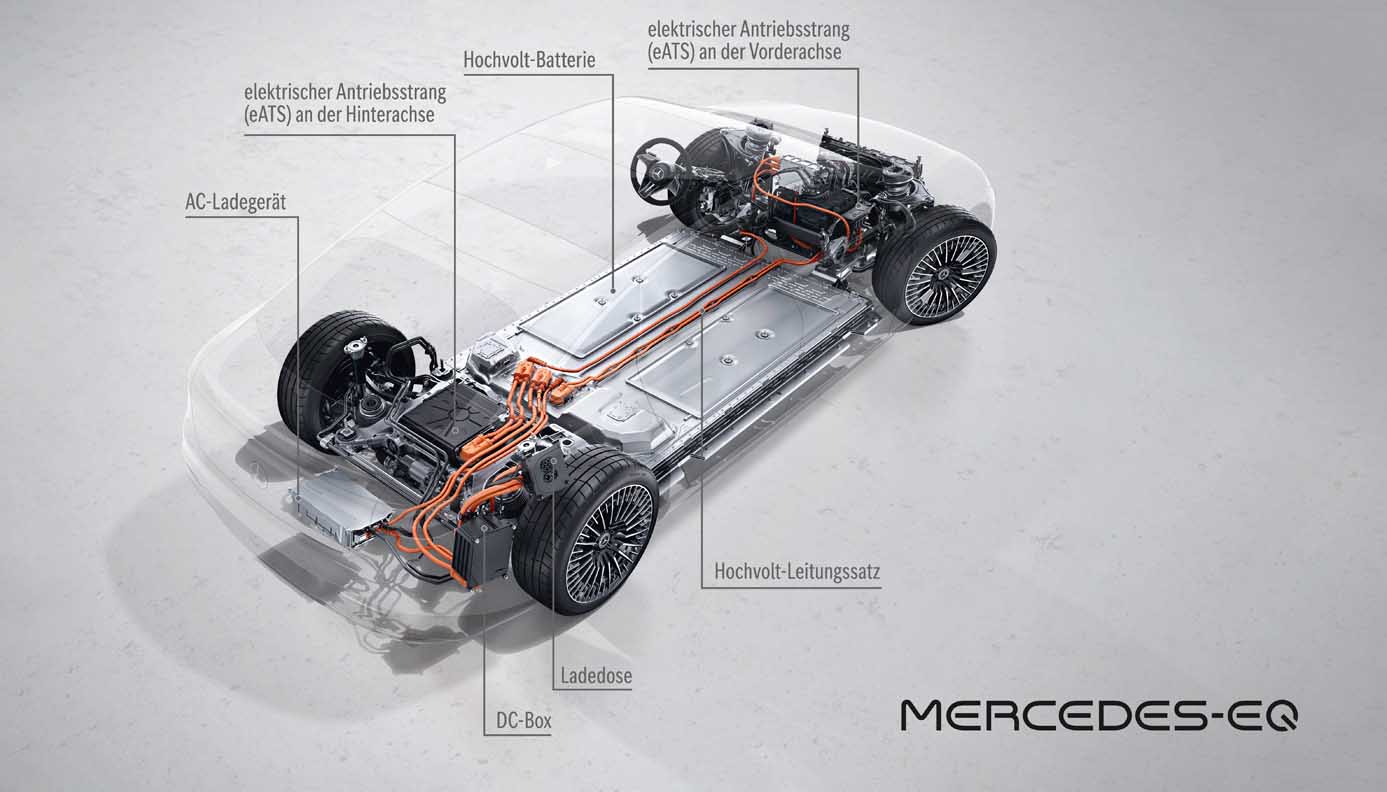
With an operating range of up to 770 kilometres (WLTP) and an output of up to 385 kW, the powertrain of the EQS also meets every expectation of a progressive saloon in the S-Class segment. All EQS models have an electric powertrain (eATS) at the rear axle, while the versions with 4MATIC also have an eATS at the front axle.
- Modular drive concept for high overall performance and long range
- EQS from Mercedes-EQ, with 245 to 385 kW plus an even more powerful performance version
- The electrical consumption1 of the EQS 450+, NEDC: combined electrical consumption:
19.1-16.0 kWh/100 km; combined CO2 emissions: 0 g/km - The electrical consumption1 of the EQS 580 4MATIC+, NEDC: combined electrical consumption: 20.0-16.9 kWh/100 km; combined CO2 emissions: 0 g/km
- Max. torque transmission output: 568 Nm (EQS 450+) resp. 855 Nm (EQS 580 4MATIC)
- WLTP ranges of up to 770 kilometres are possible depending on vehicle equipment and configuration
- Top speed limited to 210 km/h
- Available with rear- and all-wheel drive
- Electric motors on the front and rear axles are modern permanently excited synchronous motors
- Motor particularly powerful on the rear axle due to six-phase operation: two windings with three phases each
- Stators with pull-in winding for a particularly strong magnetic field
- Very compact
- Sophisticated thermal concept for high load capacity and multiple accelerations with consistently high performance
- What is known as a water lance in the shaft of the rotor cools the rotor
- Further cooling elements in the cooling circuit:
- Stator ribs
- Needle-shaped pin-fin structure on the inverter
- Transmission oil cooler: also more efficient during cold driving (gear oil is warmed up)
- 4MATIC models with Torque Shift function
- Intelligently and continuously distributes the drive torques between the front and rear axles
- Ensures that the most efficient eATS (electric drivetrain) is used in each case
- Much faster response than with mechanical all-wheel drive
- eATS can be regulated independently of each other
- Torque is checked 10,000 times per minute and set if necessary
- Intelligent recuperation
- Adjustable by the driver in three steps via shift paddles on the steering wheel
- Situation-optimised with the help of the ECO Assistant
- In DAuto, up to 5 m/s² are achieved, of which 3 m/s² are due to energy recovery (2 m/s² via the wheel brakes)
- The recuperation output is up to 290 kW4
- Braking to stop is possible
- Deceleration is also for detected vehicles travelling ahead until they come to a stop, for example at traffic lights
- In versions with rear-wheel drive, recuperation is limited by traction
- EQS meets the highest demands for noise and vibration comfort
- NVH-optimised arrangement of the magnets inside the rotors (known as sheet metal cut)
- Reduces the use of rare earths at the same time
- Special winding (known as stator tilt)
- eATS have a special foam mat all around as an NVH cover
- Cover of the inverter is a sandwich construction made of three metal and plastic layers
- eATS are double decoupled via elastomeric bearings
- Front axle: with supporting frame
- Rear axle: with carrier
- Use of acoustic foams in body-in-white construction
- Main floor under the battery
- Designed with beading for NVH reasons
- New insulation part (welded-in foam) prevents excitations
- Two acoustic dividers in the tailgate reduce booming noise
- Extensive testing at Mercedes-Benz
- Several million test kilometres on eDrive test benches in Untertürkheim
- Tough testing programme for overall vehicle testing around the globe
- Route profile/test bench profile modified compared to combustion engine to take into account torque load on the transmission in both directions (recuperation)
- Special hot/cold testing of power electronics

Because the power does not come from a socket
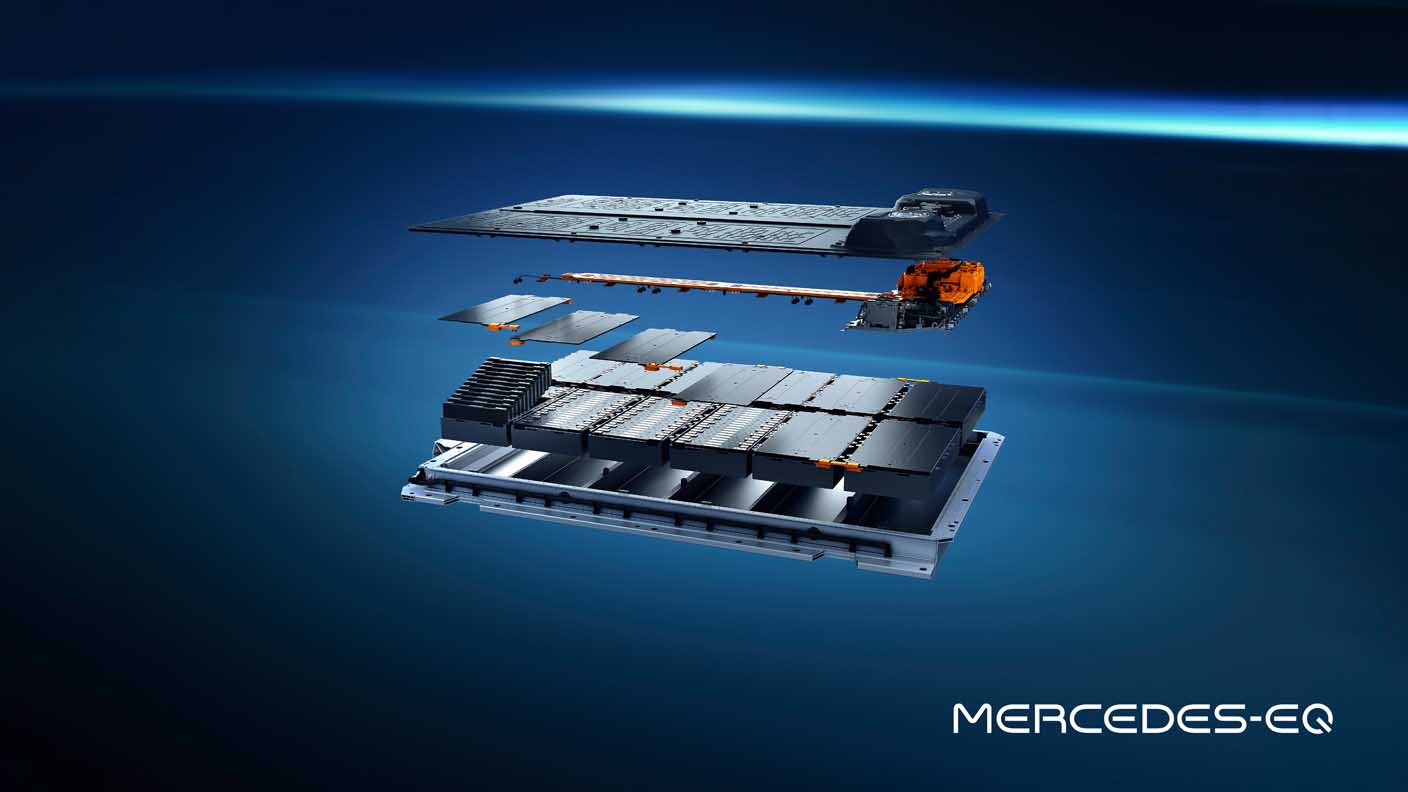
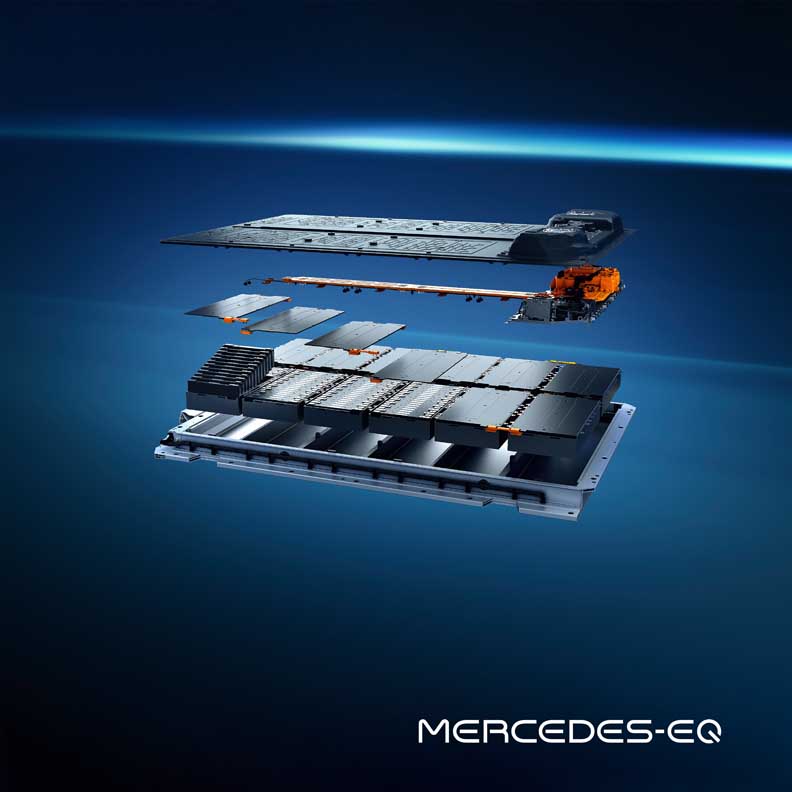
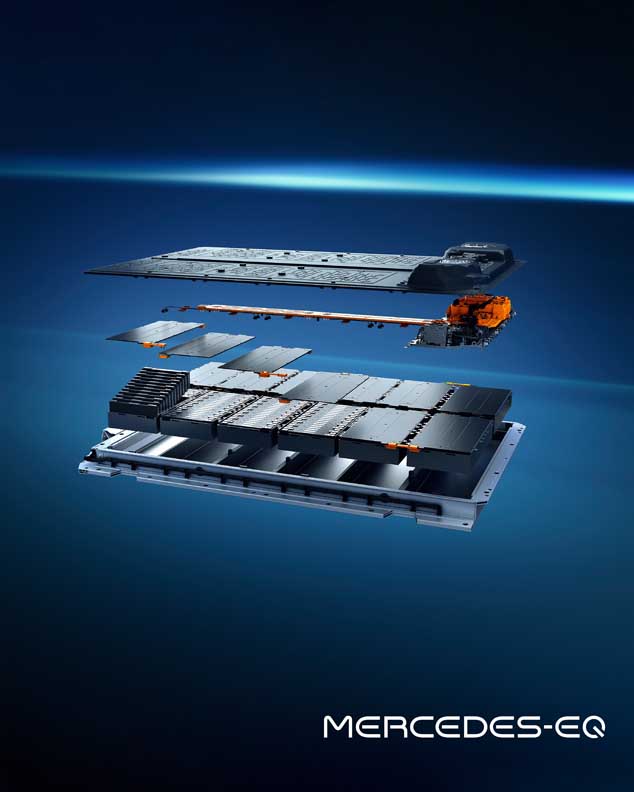
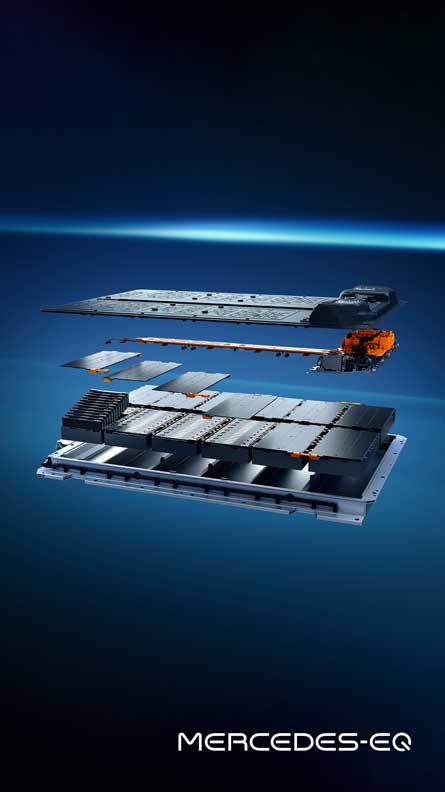
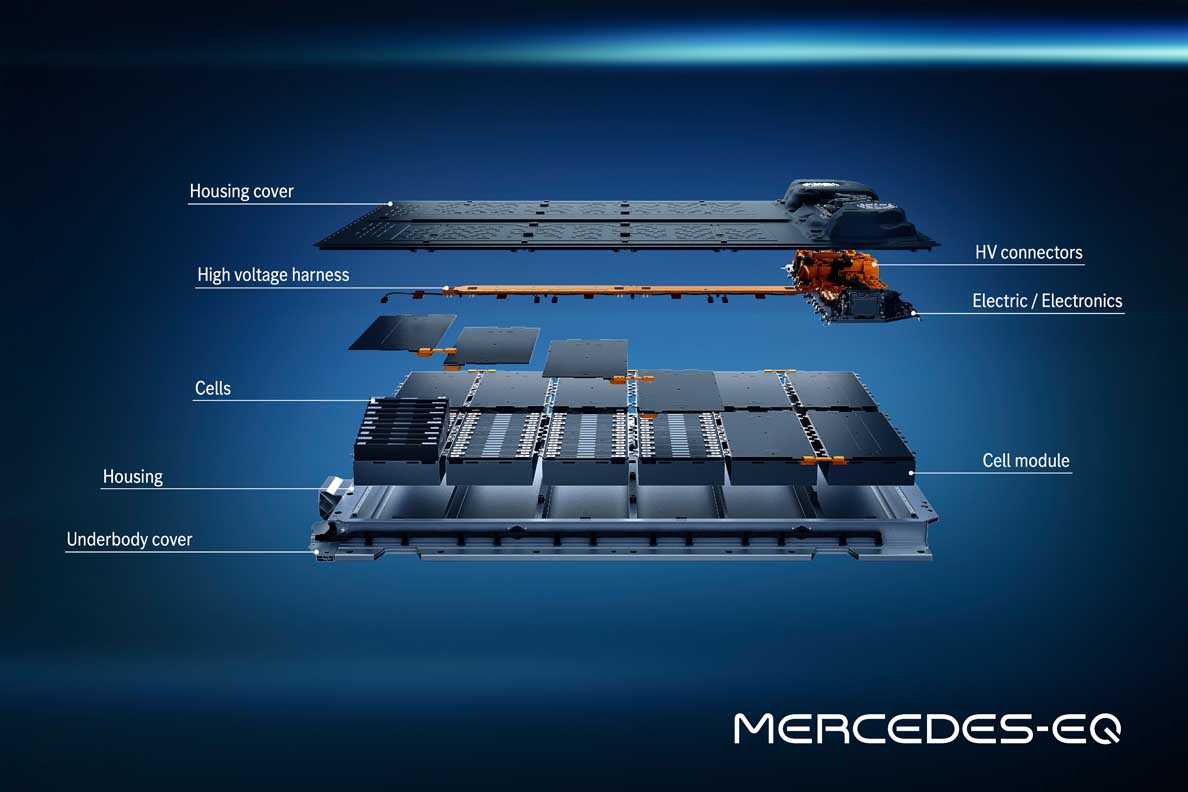
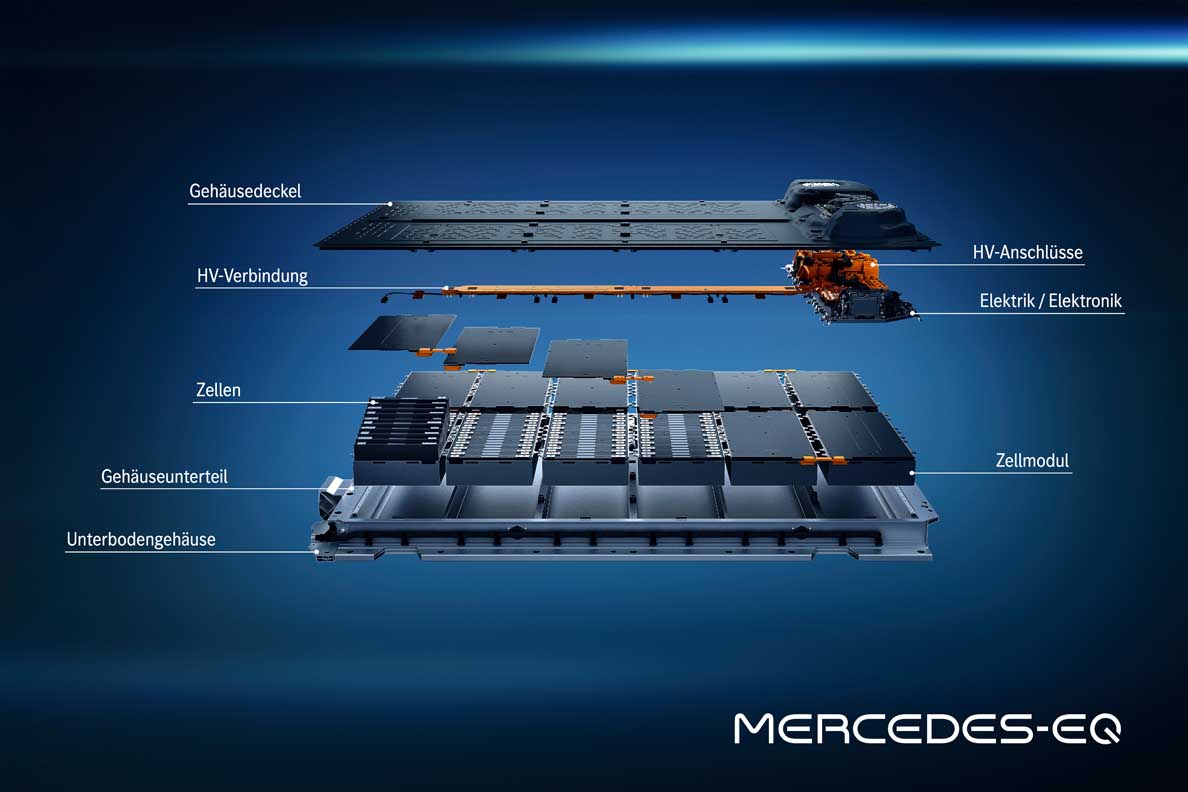
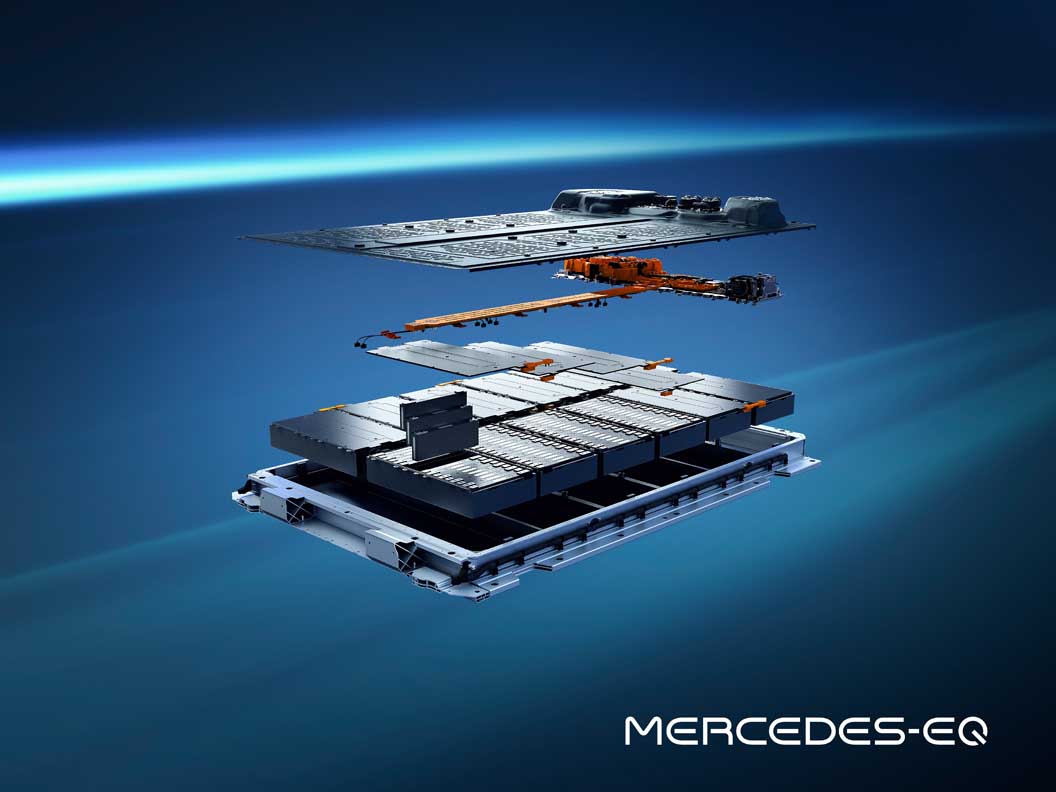
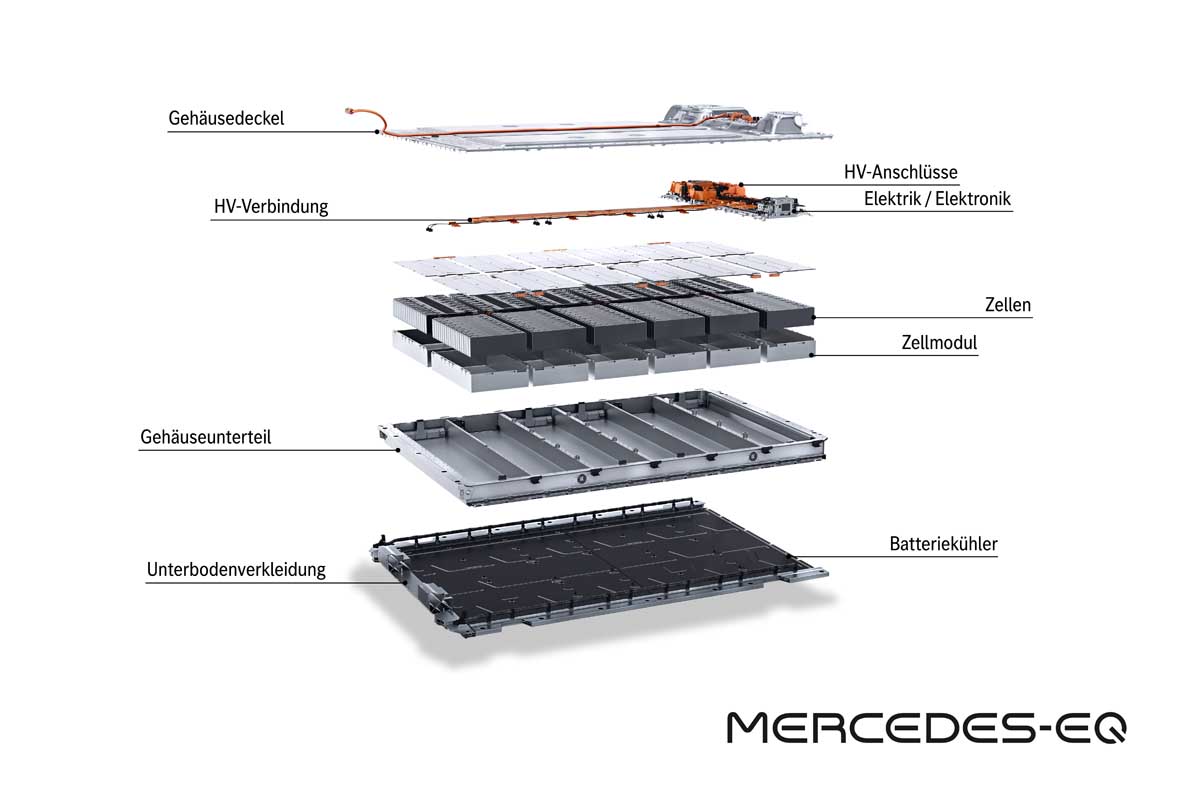
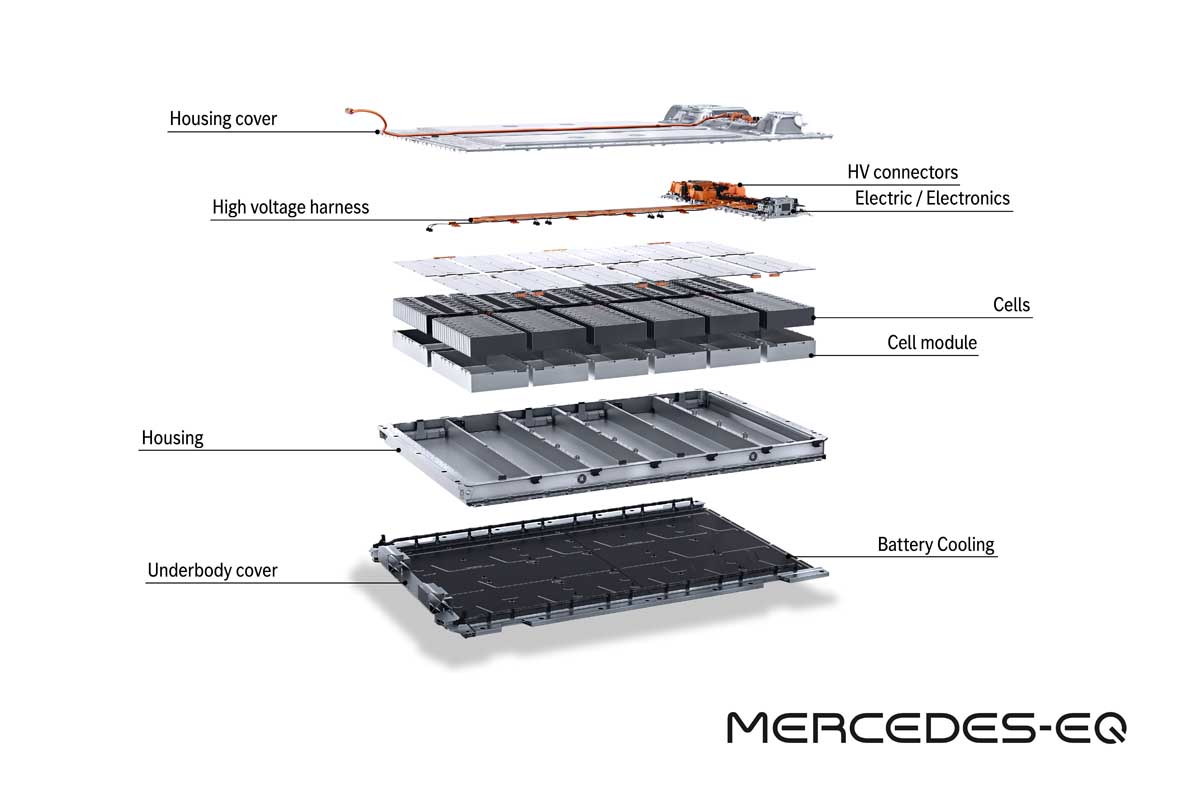
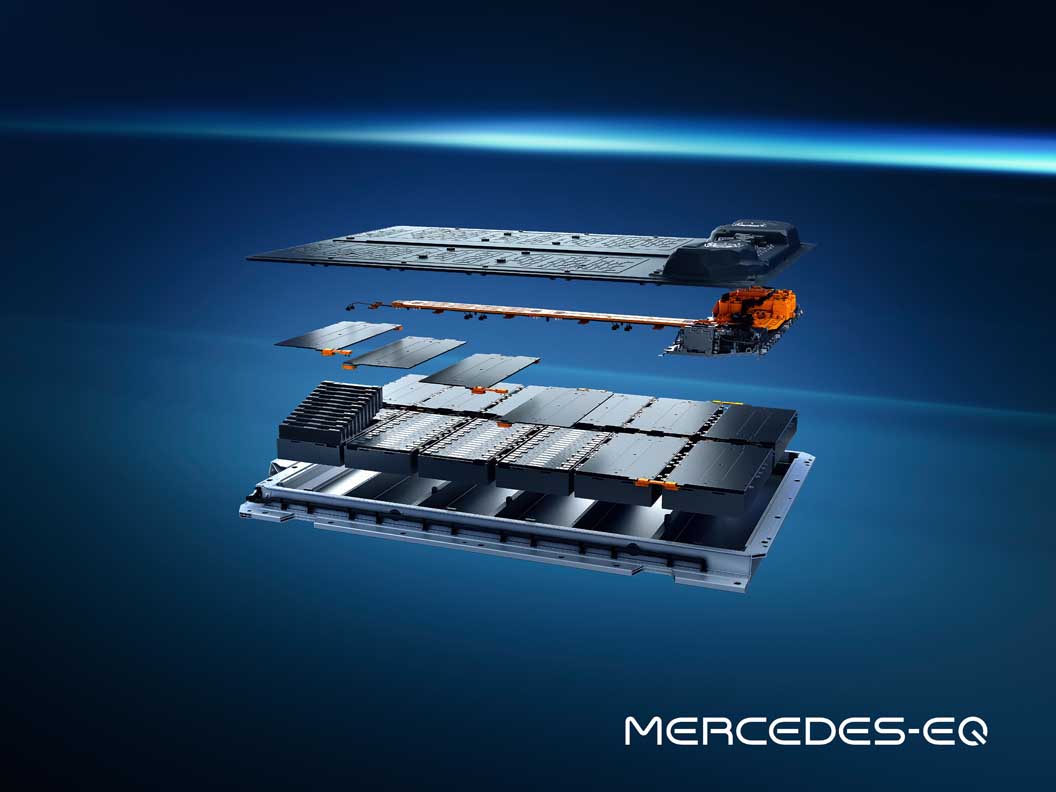
The batteries: plenty of juice on board
The EQS marks the launch of a new generation of batteries with significantly higher energy density. The larger of the two batteries has a usable energy content of 107.8 kWh. That is around 26 percent more than the EQC. The innovative battery management software, developed in-house, allows updates over the air (OTA).
The energy management of the EQS is therefore kept up to date throughout the lifecycle. A major advance in sustainability has been achieved in the cell chemistry: the proportion of cobalt has been reduced to ten percent, and the optimised active material consists of nickel, cobalt and manganese in a ratio of 8:1:1.
- New battery generation (lithium-ion technology)
- Significantly higher energy density
- Better charging performance
- In-house development
- Programming the software at the Mercedes-Benz Battery Competence Centre
- Production of battery systems in the Hedelfingen plant section at the Stuttgart-Untertürkheim site
- Modular battery concept
- Possibility of over-the-air updates for the battery management system
- 400-volt architecture
- Two battery sizes depending on power and drive (rear or 4MATIC)
- With usable energy content of 90 or 107.8 kWh
- With ten or twelve cell modules
- With pouch or hard-case cells
- Shorter charging times through intelligent thermal management when navigation is activated with Electric Intelligence
- Battery can also be preheated or cooled while driving
- Is thus in the ideal temperature window at a fast-charging station, which enables faster charging
- Coolant flows through the cavities of the aluminium extrusions of the battery frame
- PTC auxiliary heater (Positive Temperature Coefficient) integrated in cooling circuit
- Sustainability as part of the holistic battery strategy
- Optimised material mix of nickel, cobalt and manganese in a ratio of 8:1:1
- Continuous optimisation of recyclability
- Production with eco-power in Hedelfingen from 2022
- Comprehensive safety concept:
- Battery is crash-protected in the underbody
- Enclosure with energy absorbing structures at the front and side
- Stiff, double-walled base plate
- Extensive crash and component tests
- Battery, high-voltage (HV) cables and other HV components are designed and fused in such a way that they pose as little risk as possible in the event of an accident
- Battery behaviour under impact load and in the event of foreign body penetration is the test criterion
- Overheating and overcharging were simulated and tested
- Multi-stage high-voltage protection concept
- High-voltage system can be switched off automatically in case of danger
- Crash monitoring when stationary (during DC charging) is standard on the EQS
- Battery is crash-protected in the underbody
- Performance promise through battery certificate for customers
- Covers loss of capacity of the battery
- Valid for a term of ten years
- Or up 250,000 kilometres

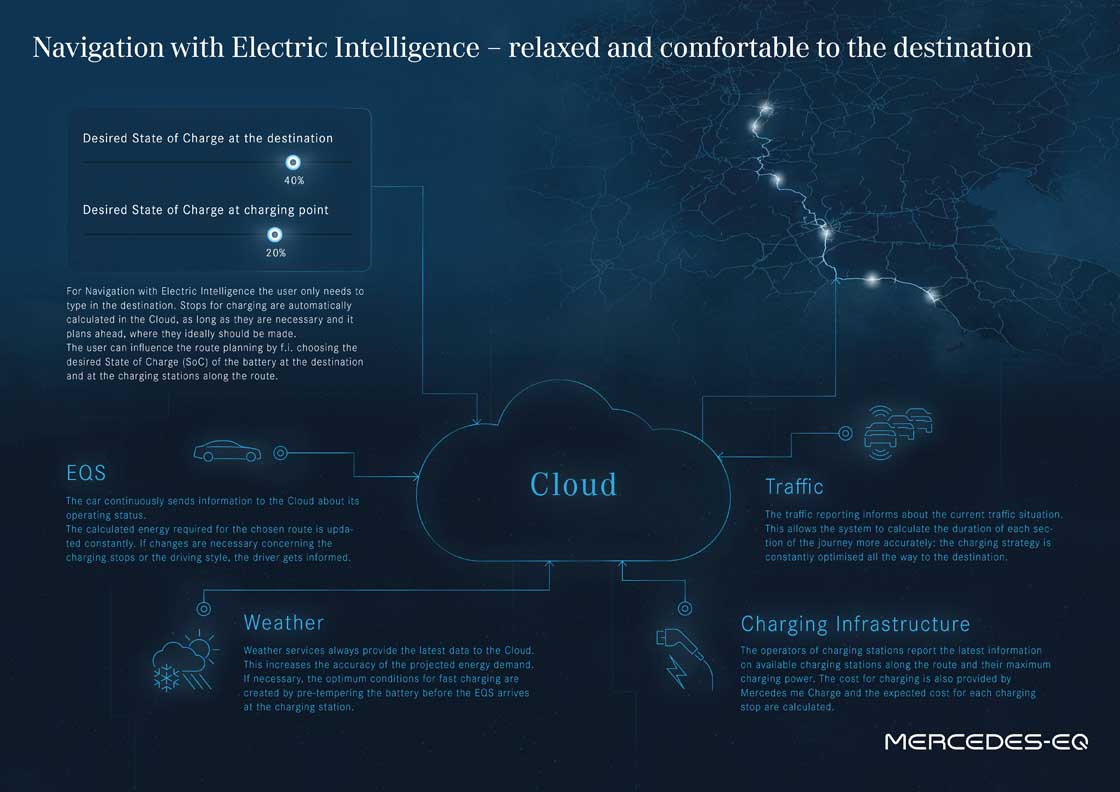
Because the shortest route is not always the fastest
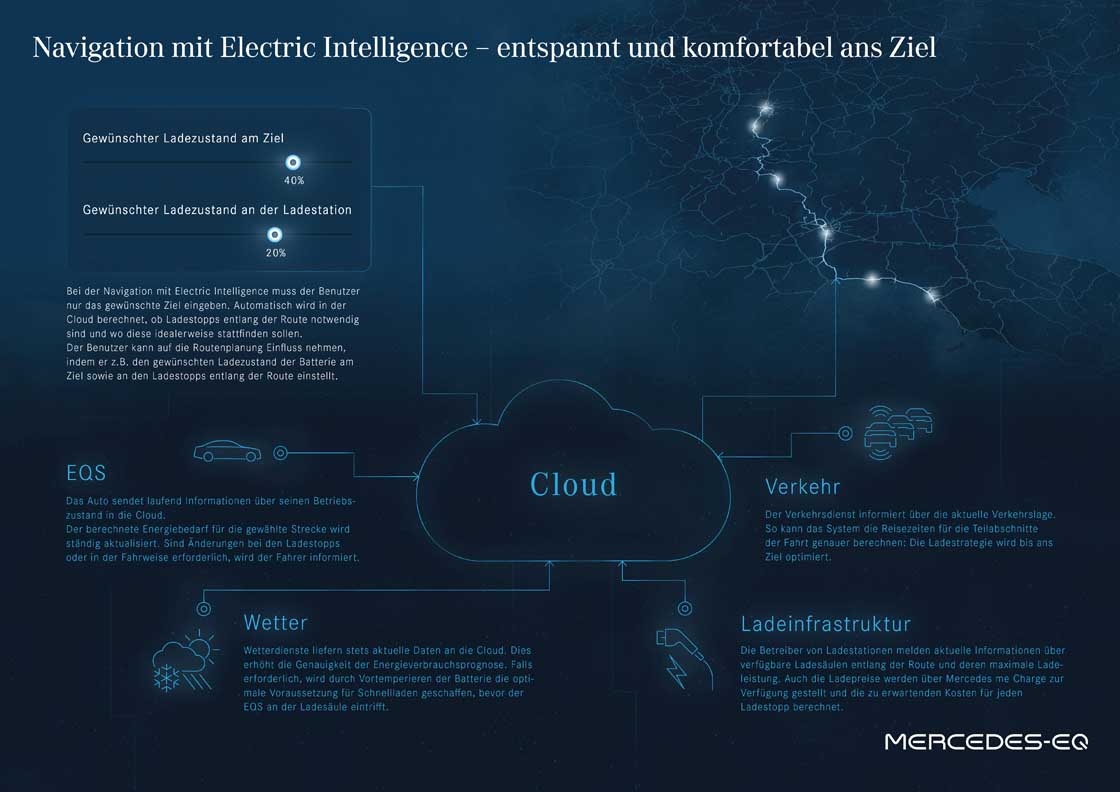
Navigation with Electric Intelligence: outsmarting traffic tailbacks
As far as Navigation with Electric Intelligence is concerned, the name says it all. Because it plans the fastest and most convenient route, including charging stops, based on numerous factors and reacts dynamically to traffic jams or a change in driving style, for example. In the EQS, navigation with Electric Intelligence is even more clever than before.
- Plans a fast and comfortable route in advance, including charging stops, based on numerous factors such as
- Calculated energy demand (topography, route, ambient temperature, speed, heating and cooling demand etc.)
- Ambient temperatures at the charging station
- Traffic situation on the planned route
- Number of charging stations available, their charging capacity and payment functions
- Responds dynamically to congestion and changes in energy demand
- Calculation in the cloud combined with on-board data
- In addition, the planned route can be edited individually
- The additional reserve at the destination and at the charging station (SoC, State of Charge) can be set, ten percent SoC is standard
- If “Charge at destination” is selected, this set reserve may be undershot at the destination
- New in the EQS
- Visualisation of whether the available battery capacity is sufficient to drive back to the starting point without charging
- Manually added charging stations along the route are given preference in route calculation
- Proposed charging stations can be excluded
- Calculation of the expected charging costs per charging stop
- Note from the “Active range monitoring” to activate ECO driving functions if there is a risk of not reaching the destination or the charging station with the selected settings

Always connected
The charging technology: where electrons silently migrate
The EQS can be charged with up to 200 kW at fast charging stations with direct current. At home or at public charging stations, the EQS can be conveniently charged with up to 22 kW with AC using the on-board charger. The EQS will also allow bidirectional charging in Japan, i.e. charging in both directions. In addition, there are various intelligent charging programs that can be activated automatically depending on the location, and functions such as particularly battery-saving charging.
- Powerful chargers
- On-board charger for alternating current with a charging capacity of up to 22 kW (optional extra)
- DC fast charging system for direct current with up to 200 kW
- Electricity for up to another 300 kilometres (WLTP) is recharged in just 15 minutes5
- High charging currents can be maintained for a long time through temperature and charging management
- New functions (see also next section on Mercedes me Charge):
- Green Charging: Mercedes me Charge thus ensures the use of energy from renewable resources for public charging
- Plug & Charge: simply plug in, and charging and billing take place automatically
- Bidirectional charging: in Japan, it will be possible to feed electricity from the vehicle back into the grid when needed
- ECO Charging: various measures reduce the battery load during charging and slow down the natural ageing process of the battery
- Charge interruption: charging process is suspended at times selected by the customer (e.g. cheaper night-time electricity can be used)

Eco-charging on the house
Mercedes me Charge: Plug & Pay
Drive to the charging station, open the flap, insert the connector and the power starts to flow: this is how easy the charging process is with the EQS, thanks to Plug & Charge. The new charging method is offered by Mercedes me Charge. Other highlights include the densest network of charging points, with more than 500,000 of them in 31 countries, and green charging. Green charging reduces the CO2 footprint in the use phase
- Plug & Charge allows particularly convenient charging of the EQS
- Charging starts automatically when the charging cable is plugged in
- Communication between vehicle and charging station takes place directly via the charging cable
- At the launch of EQS possible at IONITY in Europe
- Green charging reduces the CO2 footprint in the use phase
- With Mercedes me Charge, customers have been charging green at every public charging station throughout Europe since this year
- The charged energy quantities are balanced out with green electricity after the actual charging process
- In addition, incentives are created to invest in renewable energy systems
- In the first three years after the purchase of an EQS, there is no basic charge to customers for Mercedes me Charge and thus for green charging
- Green charging and driving can be experienced via MBUX and the Mercedes me App
- Mercedes me Charge is currently the largest charging network worldwide
- There are currently over 500,000 AC and DC charging points in 31 countries, including over 200,000 in Europe
- Integrated payment function with simple billing
- Mercedes me App has many improved and new functions since the last revision

Meet the world aerodynamics champion
Aerodynamics: only the wind knows the answer
With a cd value from 0.206 , the EQS has the best aerodynamics of any production car. The operating range particularly benefits from this. It is also among the best in terms of noise comfort. A great deal of attention to detail lies behind the very good aerodynamic and aeroacoustic performance.
- A world record. First production car with a cd value from 0.20
- Low spread of the individual models and wheels/tyres up to 22 inches
- The frontal area is 2.51 m2
- The purpose design brings numerous aerodynamic and aeroacoustic advantages
- Good coupé-like basic shape with flat windscreen
- Smooth underbody
- Lower cooling air requirement, louvre is mostly closed
- Attractively designed aero wheels are available in sizes 19, 20 and 21 inches
- A lot of aerodynamic fine tuning
- Wheel spoiler front and rear (arrow-shaped)
- Coordinated underbody panels
- Rear spoiler optimised for lift and air drag
- Extensive aerodynamics development
- By developing an entire Mercedes-EQ luxury model family, comparatively much capacity for basic development
- Several 1000 calculation runs in the virtual wind tunnel
- Approx. 700 CPUs per calculation
- Simulation helpful especially for outer skin and underbody concepts
- However, final optimisations still carried out physically in the wind tunnel with clay and hybrid models
- Due to the electrification of the powertrains, low wind noise becomes even more important
- Here, too, the EQS is among the top vehicles in its class
- Excellent aerodynamics is at the same time a good basis for low wind noise
- Extensive development steps to reduce wind noise
- Numerous optimisations in the area of door structure and door and side window seals with, for the first time, six side windows in a Mercedes
- Special acoustic comfort package with acoustically highly effective laminated glass panes
- A-pillar with specially shaped trim strip helps reduce wind noise as well as lower the cd value
- Retractable door handles

The transformers
Sustainability: thinking of tomorrow today
As part of its “Ambition 2039” initiative, Mercedes-Benz is working on offering a carbon-neutral fleet of new vehicles less than 20 years from now. By as early as 2030, the company wants more than half the cars it sells to feature electric drive systems – this includes fully electric vehicles and plug-in hybrids. In many areas, Mercedes is already thinking about tomorrow today and has designed the EQS with sustainability in mind. The vehicles are produced on a CO2-neutral basis, while resource-saving materials such as floor mats made from recycled yarn are used.
- EQS components with a total weight of more than 80 kg made of resource-saving materials (recyclates and renewable raw materials)
- Cable ducts are made of recycled plastics
- Floor coverings are made of ECONYL recycled yarn
- The aluminium for the inner part of the front bonnet has been certified by the Aluminium Stewardship Initiative (ASI) as sustainably produced
- Production of the series in Factory 56 at the Mercedes-Benz plant in Sindelfingen, the most modern automobile production facility of Mercedes-Benz
- Carbon-neutral production right from the start
- The energy requirement is reduced by a quarter compared to other assembly buildings
- Photovoltaic system with 12,000 modules can generate around 5000 kWp, covering around 30 per cent of the factory’s energy needs
- Part of the electricity flows into a DC grid that will improve the building’s energy efficiency in the future
- Connection of ventilation units and
- Connection of a stationary energy storage system based on reused vehicle batteries for intermediate storage of solar power from the photovoltaic system
- In addition to the CO2 and energy balance considerations, the sustainability approach of Mercedes-Benz in Factory 56 includes further ecological aspects
- About 40 per cent of the roof area is planted
- Intermediate storage of rainwater
- Recycled concrete was used for the first time in the concrete façade of the head-end structure
- Battery system production at the Hedelfingen annexe in Stuttgart will be CO2-neutral
from 2022
- Carbon-neutral production right from the start
- Sustainable, integrated business strategy of Mercedes-Benz considers the entire value chain
- Development
- Supplier network
- Own production
- Electrification of products
- Renewable energies for the use phase of electric vehicles
- With Ambition 2039, Mercedes-Benz is pursuing the goal of providing a fully networked and carbon-neutral vehicle fleet by 2039
- As early as 2030, the company is targeting more than 50% of passenger car sales with plug-in hybrids or purely electric vehicles
- Important milestones are carbon-neutral production in all Mercedes-Benz AG plants worldwide from 2022, the co-design of the infrastructure and the agreement of specific CO2 measures with suppliers
- Mercedes-Benz AG has had its climate protection targets confirmed by the Science Based Targets Initiative (SBTI)

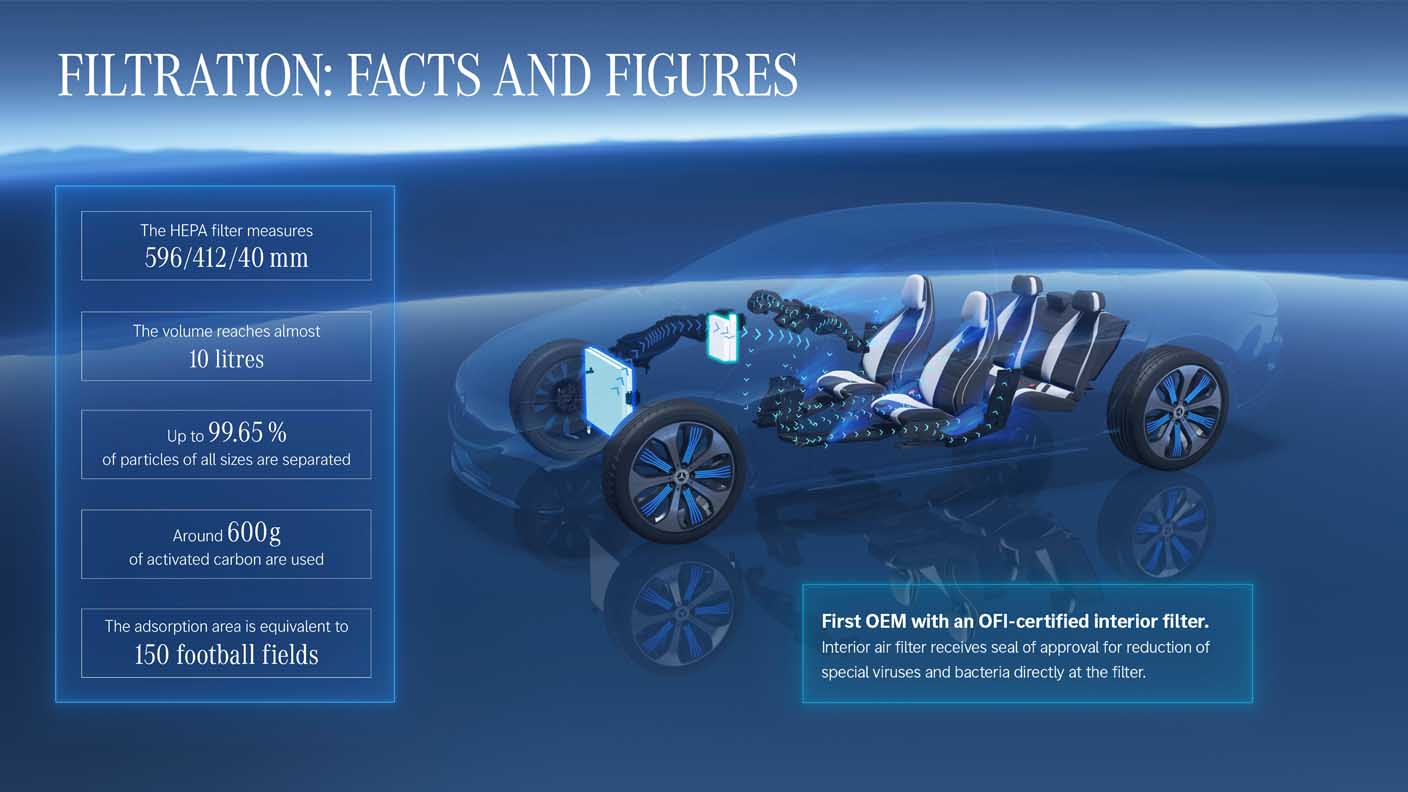
Quick guide for a full picture
Glossary: The major innovations in detail
|
eDrive test benches: This is where Mercedes-Benz tests the electric powertrain (eATS) for function, efficiency and long-term durability. On the test benches, the eATS are coupled to load machines via the drive shafts installed in the vehicle – just like the drivetrain with combustion engine and transmission on conventional test benches. At each rotational speed, they simulate different stresses on the e-drive. The testing programmes depict high-speed and road endurance runs. For this purpose, the test benches are programmed with data from real routes, topography and corresponding load conditions, for example acceleration, staying on the accelerator, kickdown or recuperation. In Untertürkheim, there are a total of 13 test benches for electric drives. Of these, seven are pure eATS test benches, where the power comes from a special direct current source, what is known as a battery simulation. On the six other test benches, the testing also includes the battery and the complete charging components of the vehicle. In addition, there are 13 test benches at the Nabern development site |
|
Electric drivetrain (eATS): An eATS basically comprises an electric motor, a (spur) transmission, the differential and the power electronics. This is compactly located on the top of the eATS. |
|
Hard-case cells: battery cells with a sturdy aluminium housing. Other designation: prismatic cells |
|
Inverter: converts the direct current (DC) of the battery into three-phase current (AC) for the electric motor. During recuperation, the e-machine generates a three-phase current that is rectified into direct current by the inverter. |
|
On-board charger: charger integrated into the vehicle that generates the direct current required by the battery from the alternating current of the power grid. |
|
Permanently excited synchronous machines (PSM): with PSM, the rotor of the AC motor is fitted with permanent magnets and therefore does not need to be supplied with power. The magnets – and thus the rotor – follow the rotating alternating current field in the winding of the stator. The engine is said to be synchronous, because the rotor turns at the same rate as the magnetic field of the stator. The frequency is adjusted in the power electronics inverters to the speed requirements of the driver. The advantages of this design include high power density, high efficiency and high power constancy. |
|
Pouch cells: battery cells with a flexible, bag-like cover made of aluminium and a second, insulating foil. Other designation: coffee bag cells |
|
Recuperation: in this energy recovery process, the high-voltage battery is charged by converting the mechanical rotary motion of the wheels in the drive systems into electrical energy during overrun or braking operation. |
|
Stator tilt: in relation to the permanent magnets of the rotor, the coils of the stator are obliquely wound. This is advantageous for NVH behaviour (Noise, Vibration, Harshness), especially at low speeds. Otherwise, what is known as cogging torque could occur. This would lead to fine but unpleasant vibrations when driving very slowly. |